Psychologist
Abraham Maslow introduced the concept of a Hierarchy of Needs. His hierarchy
proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to
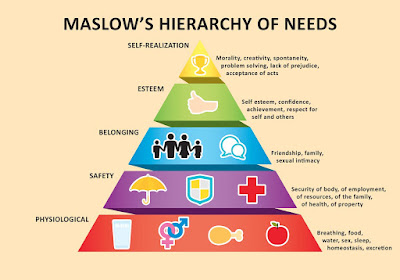
meet higher level growth needs. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is most often
displayed as a hierarchical pyramid with five levels. However, the most recent
depictions of the hierarchical pyramid have seven or eight levels. But, no
matter which pyramid you review, the lowest levels of the pyramid are made up
of the most basic needs, while the more complex needs are located at the top of
the pyramid. The four lower levels of all the pyramids are considered
physiological or deficiency needs, while the top level(s) are considered growth
needs. Maslow’s believes that the lower
level needs have to be satisfied before higher needs can influence behavior.
Maslow’s Theory of Motivation
The
basis of Maslow’s theory of motivation is that human beings are motivated by
unsatisfied needs, and that certain lower needs need to be satisfied before
higher needs can be addressed. Needs at the bottom of the pyramid are basic
physical requirements including the need for food, air, water, and sleep. Once
these lower-level needs have been met, people can move on to the next level of
needs, which are for safety and security. Once these needs have been reasonably
satisfied, he or she may be able to reach the next level, and eventually after
all the lower needs are met, they can reach the highest level called
self-actualization. Maslow’s believed that all people are motivated to move up
the hierarchy toward a level of self-actualization. Unfortunately, progress is often disrupted by
the in ability to meet lower level needs. He believed a person cannot become
self-actualized if he or she is starving for food or if they are still seeking
love and affection from others.
Physiological Needs
Physiological
needs deal with the maintenance of the human body. This lowest category
includes the most basic needs that are vital to survival, such as the need for
water, air, food, and sleep. Maslow believed that these needs are the most
instinctive needs because all needs become secondary until these needs are met.
If we need water, then little else matters until we have something to drink.
Safety and Security Needs
Safety
and security needs are about keeping us safe from harm. These needs include
shelter, job security, health, and safe environments. If a person does not feel
safe in an environment, they will seek to find safety before they attempt to
meet any higher level needs. These security needs are important for survival,
but they are not as important as the basic physiological needs.
Social Needs/ Love and Belongings
Social
needs advance our tribal nature. These are the needs for belonging, love,
affection as well as for relationships with family and friends and
companionship. These needs are met through pleasing and fulfilling
relationships with others. A pleasing and fulfilling relationship would imply
acceptance by others. Having satisfied their basic physiological and security
needs, people can seek relationships from which their need for love and
belonging can be met.
Self-Esteem
Humans
chase individualized goals in life but the need for fulfillment is rooted in us
all. Without the confidence, self-love, and meaning, it is difficult to reach
our desires. This sector of the pyramid relies on the steps below it and is
crucial to the top of the pyramid.
Self-Actualization
Final
step as the top of Mount Everest. Everyone climbs through the steps of life and
ultimately looks to maximize on their potential. Without the four steps below,
self-actualization is unreachable and potential can’t be reached.
Conclusion
Maslow’s
Hierarchy of Needs explains that people have certain needs that have to be met,
and their needs are ranked. Lower needs
include survival needs like air, food, and water, and higher needs include
self-esteem. The highest need is self-actualization,
which means that a person feels he has met his potential. The needs in order are: physiological,
safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization.
References
Ø Wageman, R. (1997) ‘Critical
success factors for creating superb self-managing teams.’
Organizational Dynamics, 26 (1):
49-62.
Ø A.H. Maslow, "Critique of
self-actualization theory", in: E. Hoffman (Ed.), Future visions: The unpublished
papers of Abraham Maslow (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1996), pp. 26–32
Ø Wahba, M. A.; Bridwell, L. G.
(1976). "Maslow reconsidered: A review of research on the need hierarchy
theory". Organizational Behavior and Human Performance. 15 (2): 212–240
Ø Tay, L.; Diener, E. (2011).
"Needs and subjective well-being around the world". Journal of
Personality and Social Psychology. 101 (2): 354–365.
Ø Goebel, B. L.; Brown, D. R. (1981).
"Age differences in motivation related to Maslow's need hierarchy".
Developmental Psychology. 17: 809–815.
Ø A Theory of Human Motivation,
original 1943 article by Maslow



Dear Dilmi. Maslows Hierarchy of need matched in any situation. We all as human beings seek satisfaction for above needs in different levels. However my personal idea is Needs are not always coming one before one on Hierarchical manner. This order can be changed due several factors.
ReplyDeleteGeographical area
Religion
Age
Gender
and many factors will effect the order of this needs.
As an example if we consider a Child in Palasthine (War affected area), he or she doesn't care the Physiological needs. They are seeking for Safety needs 1st.
Likewise this order may be changed . However majority of needs are in line with Maslow s hierarchical theory
Yes Janaka, as you said each and every human being is climbing over the levels of these needs. However fulfilling the same is depending on the situation which they are facing and priority given to fulfill the each need.
DeleteDear Dilmi,
ReplyDeleteIt's a good article since it’s one of the most important and applicable theories in psychology.
I also think that, to a degree, every person is different. But it can still be used as a basic guide map to human behavior.
Obviously, if a person is starving to death they aren’t going to be worried as much about their own safety.
If a person is living in life threatening conditions, they’re going to probably be too focused on their own survival than whether they have a sense of belonging in society.
Yes Nishantha, this theory speaks about chapters in the human life or the behavior. However fulfillment of each need depends on the expectations and situation of each human being
ReplyDelete